dom(布局模块)

此模块定义了一组层次化的 ftxui::Element(元素)。元素管理布局,并且可以响应终端尺寸变化。请注意以下使用此模块创建简单布局并运用多个操作符的示例:
@subpage module-dom-examples 章节提供了一系列示例。
示例:
namespace ftxui {
...
// 定义文档
Element document = vbox({
text("窗口") | bold | color(Color::Blue),
gauge(0.5)
text("页脚")
});
// 通过调用 `ftxui::border` 装饰器函数添加边框。
document = border(document);
// 使用管道操作符添加另一个边框。
document = document | border.
// 使用 |= 操作符添加另一个边框。
document |= border
...
}元素列表
所有元素均已包含,可通过引入相应的头文件访问:
#include <ftxui/dom/elements.hpp>\include{strip} “ftxui/dom/elements.hpp”
文本
最简单的控件。它显示文本。
text("我是一段文本");我是一段文本。垂直文本
与 ftxui::text 相同,但垂直显示。
代码:
vtext("你好");终端输出:
你
好段落
类似于 ftxui::text,但会根据容器的宽度将单个单词沿多行换行。
示例代码:
paragraph("一段很长的文本")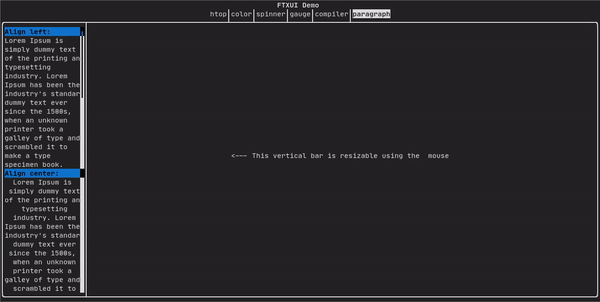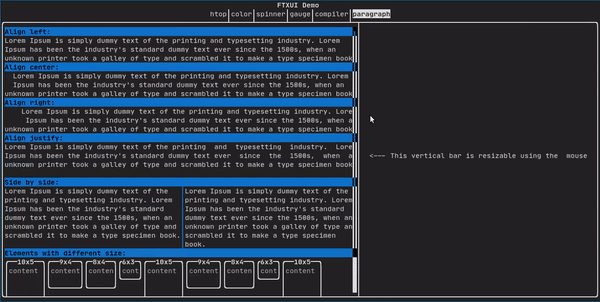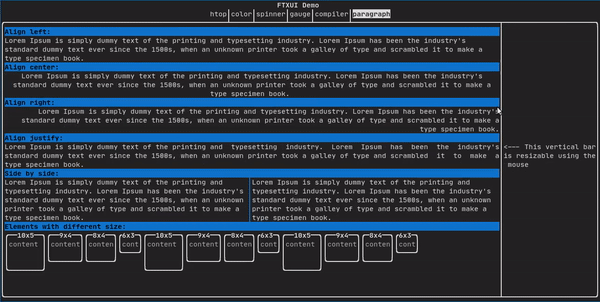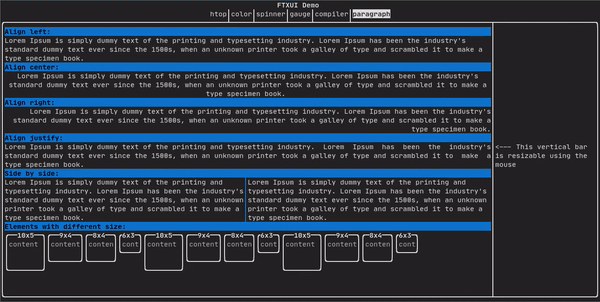
更详细的示例请参阅详细示例。段落还包括许多其他变体,如下所示:
namespace ftxui {
Element paragraph(std::string text);
Element paragraphAlignLeft(std::string text);
Element paragraphAlignRight(std::string text);
Element paragraphAlignCenter(std::string text);
Element paragraphAlignJustify(std::string text);
}边框
在元素周围添加边框。
代码:
border(text("元素"))终端输出:
┌──────┐
│元素 │
└──────┘Note
您可以使用管道操作符实现相同的行为。
代码:
text("元素") | border边框还有多种样式,如下所示:
namespace ftxui {
Element border(Element);
Element borderLight(Element);
Element borderHeavy(Element);
Element borderDouble(Element);
Element borderRounded(Element);
Element borderEmpty(Element);
Decorator borderStyled(BorderStyle);
Decorator borderWith(Pixel);
}窗口
ftxui::window 是一个带有额外标题的 ftxui::border。要在元素周围添加窗口,请将其包装并指定一个字符串作为标题。
代码:
window("窗口", text("元素"))终端输出:
┌窗口─┐
│元素 │
└─────┘分隔符
显示垂直/水平线,以视觉上将容器的内容分成两部分。
代码:
border(
hbox({
text("左"),
separator(),
text("右")
})
)终端输出:
┌──┬──┐
│左│右│
└──┴──┘分隔符有多种样式,如下所示:
namespace ftxui {
Element separator(void);
Element separatorLight();
Element separatorHeavy();
Element separatorDouble();
Element separatorEmpty();
Element separatorStyled(BorderStyle);
Element separator(Pixel);
Element separatorCharacter(std::string);
Element separatorHSelector(float left,
float right,
Color background,
Color foreground);
Element separatorVSelector(float up,
float down,
Color background,
Color foreground);
}进度条
这是一个表示进度比例的视觉元素。
代码:
border(gauge(0.5))终端输出:
┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│██████████████████████████████████████ │
└────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘进度条可以多种方向显示,如下所示:
namespace {
Element gauge(float ratio);
Element gaugeLeft(float ratio);
Element gaugeRight(float ratio);
Element gaugeUp(float ratio);
Element gaugeDown(float ratio);
Element gaugeDirection(float ratio, GaugeDirection);
}图表
@htmlonly
@endhtmlonly
参见:
Element graph(GraphFunction);颜色
大多数终端控制台可以显示彩色文本和彩色背景。FTXUI 支持所有调色板:
Decorator color(Color);
Decorator bgcolor(Color);颜色图库:
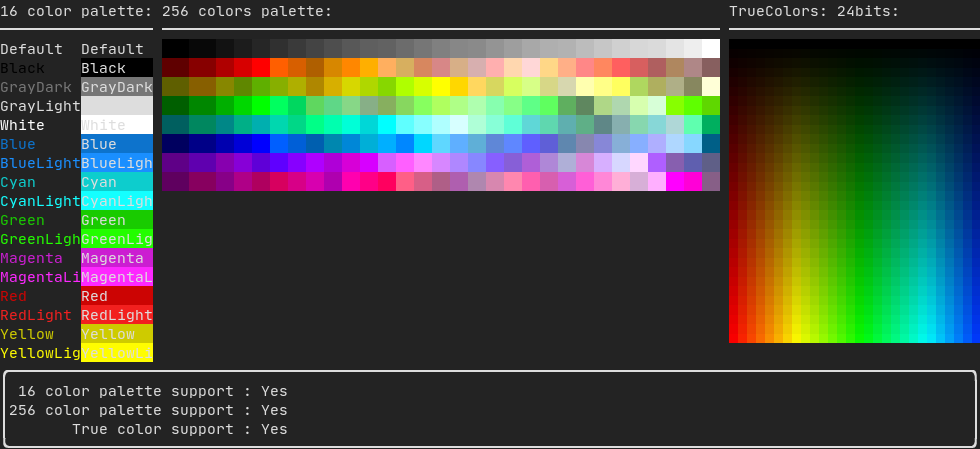
16色调色板
大多数终端支持以下颜色:
默认色
黑色
深灰色
浅灰色
白色
蓝色
亮蓝色
青色
亮青色
绿色
亮绿色
洋红色
亮洋红色
红色
亮红色
黄色
亮黄色
使用管道操作符应用上述颜色的示例:
text("蓝色前景") | color(Color::Blue);
text("蓝色背景") | bgcolor(Color::Blue);
text("黑底白字") | color(Color::Black) | bgcolor(Color::White);256色调色板
支持256色的终端。 @htmlonly
@endhtmlonly
text("亮粉色") | color(Color::HotPink);真彩色
支持真彩色的终端,您可以直接使用24位RGB色彩空间:
使用以下构造函数指定颜色的RGB或HSV值:
有两个构造函数:
ftxui::Color::RGB(uint8_t red, uint8_t green, uint8_t blue);
ftxui::Color::HSV(uint8_t hue, uint8_t saturation, uint8_t value);@htmlonly
@endhtmlonly
线性渐变
FTXUI 支持线性渐变。可应用于前景或背景。
Decorator color(const LinearGradient&);
Decorator bgcolor(const LinearGradient&);ftxui::LinearGradient 由角度(度)和颜色停止点列表定义。
auto gradient = LinearGradient()
.Angle(45)
.AddStop(0.0, Color::Red)
.AddStop(0.5, Color::Green)
.AddStop(1.0, Color::Blue);您也可以使用简化的构造函数:
LinearGradient(Color::Red, Color::Blue);LinearGradient(45, Color::Red, Color::Blue);参见演示。
样式
除了彩色文本和彩色背景外,许多终端还支持文本效果,例如:bold(粗体)、italic(斜体)、dim(暗淡)、underlined(下划线)、inverted(反色)、blink(闪烁)。
Element bold(Element);
Element italic(Element);
Element dim(Element);
Element inverted(Element);
Element underlined(Element);
Element underlinedDouble(Element);
Element strikethrough(Element);
Element blink(Element);
Decorator color(Color);
Decorator bgcolor(Color);
Decorator colorgrad(LinearGradient);
Decorator bgcolorgrad(LinearGradient);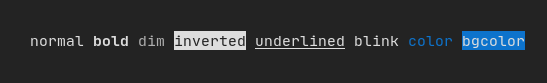
要使用这些效果,只需用所需的效果包装您的元素:
underlined(bold(text("此文本为粗体并带下划线")))或者,使用管道操作符将其链接到您的元素:
text("此文本为粗体") | bold | underlined布局
使元素能够以以下方式排列:
- 使用
ftxui::hbox水平排列 - 使用
ftxui::vbox垂直排列 - 使用
ftxui::gridbox在网格中排列 - 使用
ftxui::flexbox沿一个方向环绕排列。
使用 ftxui::hbox、ftxui::vbox 和 ftxui::filler 的示例。

使用 ftxui::gridbox 的示例:

使用 flexbox 的示例:

元素也可以使用 ftxui::flex 装饰器变得灵活。
代码:
hbox({
text("左") | border ,
text("中") | border | flex,
text("右") | border,
});终端输出:
┌──┐┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐┌───┐
│左││中 ││右│
└──┘└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘└───┘代码:
hbox({
text("左") | border ,
text("中") | border | flex,
text("右") | border | flex,
});终端输出:
┌──┐┌───────────────────────────────┐┌───────────────────────────────┐
│左││中 ││右 │
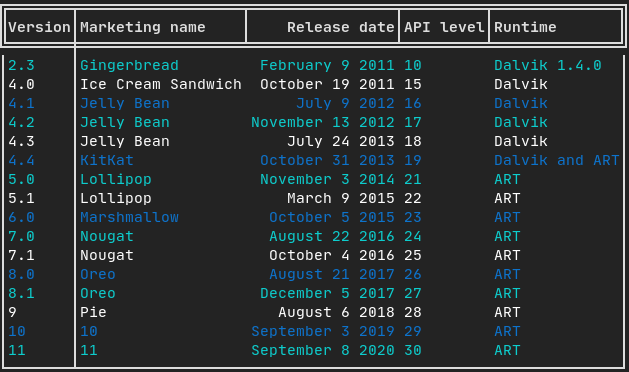
└──┘└───────────────────────────────┘└───────────────────────────────┘表格
能够轻松地将数据格式化为整洁的表格状视觉形式。
代码示例:
画布
参见 API <ftxui/dom/canvas.hpp>
auto c = Canvas(100, 100);
c.DrawPointLine(10, 10, 80, 10, Color::Red);
auto element = canvas(c);可以在 ftxui::Canvas 上使用盲文、方块或简单字符进行绘制:
简单示例:
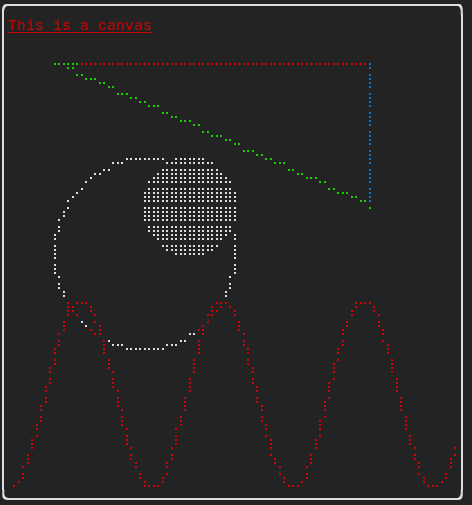
复杂示例: